Serving Recommendation Framework#
Architecture of the serving pipelines#
The diagram below demonstrates the components of the friesian serving system, which typically consists of three stages:
Offline: Preprocess the data to get user/item DNN features and user/item Embedding features. Then use the embedding features and embedding model to get embedding vectors.
Nearline: Retrieve user/item profiles and keep them in the Key-Value store. Retrieve item embedding vectors and build the faiss index. Make updates to the profiles from time to time.
Online: Trigger the recommendation process whenever a user comes. Recall service generate candidates from millions of items based on embeddings and the deep learning model ranks the candidates for the final recommendation results.
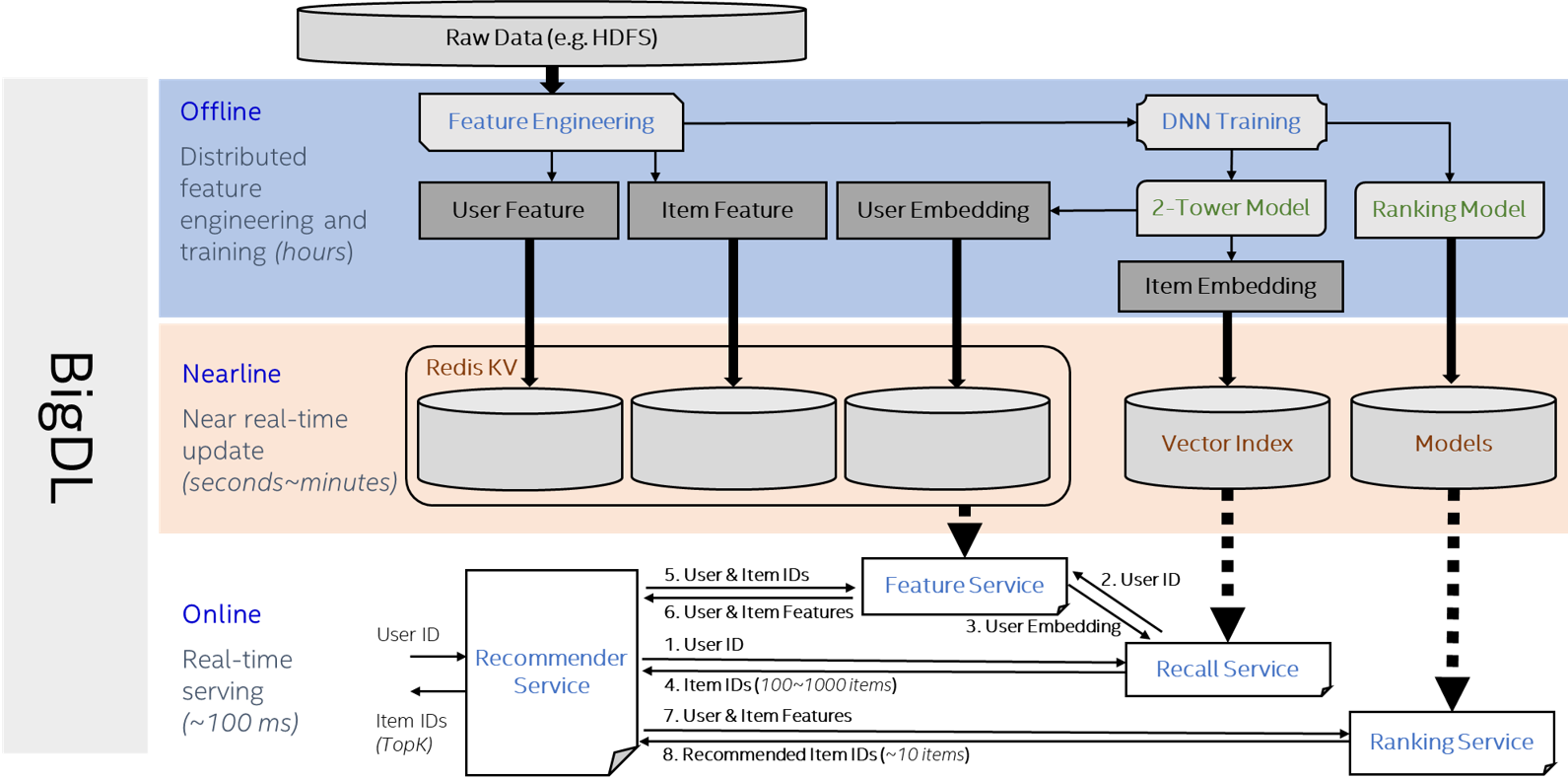
Services and APIs#
The friesian serving system consists of 4 types of services:
Ranking Service: performs model inference and returns the results.
rpc doPredict(Content) returns (Prediction) {}Input: The
encodeStris a Base64 string encoded from a bigdl Activity serialized byte array.
message Content { string encodedStr = 1; }
Output: The
predictStris a Base64 string encoded from a bigdl Activity (the inference result) serialized byte array.
message Prediction { string predictStr = 1; }
Feature Service: searches user embeddings, user features or item features in Redis, and returns the features.
rpc getUserFeatures(IDs) returns (Features) {}andrpc getItemFeatures(IDs) returns (Features) {}Input: The user/item id list for searching.
message IDs { repeated int32 ID = 1; }
Output:
colNamesis a string list of the column names.b64Featureis a list of Base64 string, each string is encoded from java serialized array of objects.IDis a list of ids correspondingb64Feature.
message Features { repeated string colNames = 1; repeated string b64Feature = 2; repeated int32 ID = 3; }
Recall Service: searches item candidates in the built faiss index and returns candidates id list.
rpc searchCandidates(Query) returns (Candidates) {}Input:
userIDis the id of the user to search similar item candidates.kis the number of candidates.
message Query { int32 userID = 1; int32 k = 2; }
Output:
candidateis the list of ids of item candidates.
message Candidates { repeated int32 candidate = 1; }
Recommender Service: gets candidates from the recall service, calls the feature service to get the user and item candidate’s features, then sorts the inference results from ranking service and returns the top recommendNum items.
rpc getRecommendIDs(RecommendRequest) returns (RecommendIDProbs) {}Input:
IDis a list of user ids to recommend.recommendNumis the number of items to recommend.candidateNumis the number of generated candidates to inference in ranking service.
message RecommendRequest { int32 recommendNum = 1; int32 candidateNum = 2; repeated int32 ID = 3; }
Output:
IDProbListis a list of results corresponding to userIDin input. EachIDProbsconsists ofIDandprob,IDis the list of item ids, andprobis the corresponding probability.
message RecommendIDProbs { repeated IDProbs IDProbList = 1; } message IDProbs { repeated int32 ID = 1; repeated float prob = 2; }
Quick Start#
You can run Friesian Serving Recommendation Framework using the official Docker images.
You can follow the following steps to run the WnD demo.
Pull docker image from dockerhub
docker pull intelanalytics/friesian-grpc:0.0.2
Run & enter docker container
docker run -itd --name friesian --net=host intelanalytics/friesian-grpc:0.0.2 docker exec -it friesian bash
Add vec_feature_user_prediction.parquet, vec_feature_item_prediction.parquet, wnd model, wnd_item.parquet and wnd_user.parquet (You can check the schema of the parquet files)
Start ranking service
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=1 java -cp bigdl-friesian-serving-spark_2.4.6-0.14.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.intel.analytics.bigdl.friesian.serving.ranking.RankingServer -c config_ranking.yaml > logs/inf.log 2>&1 &
Start feature service for recommender service
./redis-5.0.5/src/redis-server & java -Dspark.master=local[*] -cp bigdl-friesian-serving-spark_2.4.6-0.14.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.intel.analytics.bigdl.friesian.serving.feature.FeatureServer -c config_feature.yaml > logs/feature.log 2>&1 &
Start feature service for recall service
java -Dspark.master=local[*] -cp bigdl-friesian-serving-spark_2.4.6-0.14.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.intel.analytics.bigdl.friesian.serving.feature.FeatureServer -c config_feature_vec.yaml > logs/fea_recall.log 2>&1 &
Start recall service
java -Dspark.master=local[*] -Dspark.driver.maxResultSize=2G -cp bigdl-friesian-serving-spark_2.4.6-0.14.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.intel.analytics.bigdl.friesian.serving.recall.RecallServer -c config_recall.yaml > logs/vec.log 2>&1 &
Start recommender service
java -cp bigdl-friesian-serving-spark_2.4.6-0.14.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.intel.analytics.bigdl.friesian.serving.recommender.RecommenderServer -c config_recommender.yaml > logs/rec.log 2>&1 &
Check if the services are running
ps aux|grep friesianYou will see 5 processes start with ‘java’
Run client to test
java -Dspark.master=local[*] -cp bigdl-friesian-serving-spark_2.4.6-0.14.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.intel.analytics.bigdl.friesian.serving.recommender.RecommenderMultiThreadClient -target localhost:8980 -dataDir wnd_user.parquet -k 50 -clientNum 4 -testNum 2
Close services
ps aux|grep friesian (find the service pid) kill xxx (pid of the service which should be closed)
Schema of the parquet files#
The schema of the user and item embedding files#
The embedding parquet files should contain at least 2 columns, id column and prediction column. The id column should be IntegerType and the column name should be specified in the config files. The prediction column should be DenseVector type, and you can transfer your existing embedding vectors using pyspark:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import udf, col
from pyspark.ml.linalg import VectorUDT, DenseVector
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.master("local[*]") \
.config("spark.driver.memory", "2g") \
.getOrCreate()
df = spark.read.parquet("data_path")
def trans_densevector(data):
return DenseVector(data)
vector_udf = udf(lambda x: trans_densevector(x), VectorUDT())
# suppose the embedding column (ArrayType(FloatType,true)) is the existing user/item embedding.
df = df.withColumn("prediction", vector_udf(col("embedding")))
df.write.parquet("output_file_path", mode="overwrite")
The schema of the recommendation model feature files#
The feature parquet files should contain at least 2 columns, the id column and other feature columns. The feature columns can be int, float, double, long and array of int, float, double and long. Here is an example of the WideAndDeep model feature.
+-------------+--------+--------+----------+--------------------------------+---------------------------------+------------+-----------+---------+----------------------+-----------------------------+
|present_media|language|tweet_id|tweet_type|engaged_with_user_follower_count|engaged_with_user_following_count|len_hashtags|len_domains|len_links|present_media_language|engaged_with_user_is_verified|
+-------------+--------+--------+----------+--------------------------------+---------------------------------+------------+-----------+---------+----------------------+-----------------------------+
| 9| 43| 924| 2| 6| 3| 0.0| 0.1| 0.1| 45| 1|
| 0| 6| 4741724| 2| 3| 3| 0.0| 0.0| 0.0| 527| 0|
+-------------+--------+--------+----------+--------------------------------+---------------------------------+------------+-----------+---------+----------------------+-----------------------------+
The data schema in Redis#
The user features, item features and user embedding vectors are saved in Redis. The data saved in Redis is a key-value set.
Key in Redis#
The key in Redis consists of 3 parts: key prefix, data type, and data id.
Key prefix is
redisKeyPrefixspecified in the feature service config file.Data type is one of
useroritem.Data id is the value of
userIDColumnoritemIDColumn. Here is an example of key:2tower_user:29
Value in Redis#
A row in the input parquet file will be converted to java array of object, then serialized into byte array, and encoded into Base64 string.
Data schema entry#
Every key prefix and data type combination has its data schema entry to save the corresponding column names. The key of the schema entry is keyPrefix + dataType, such as 2tower_user. The value of the schema entry is a string of column names separated by ,, such as enaging_user_follower_count,enaging_user_following_count,enaging_user_is_verified.
Config for different service#
You can pass some important information to services using -c config.yaml
java -Dspark.master=local[*] -Dspark.driver.maxResultSize=2G -cp bigdl-friesian-serving-spark_2.4.6-0.14.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.intel.analytics.bigdl.friesian.serving.recall.RecallServer -c config_recall.yaml
Ranking Service Config#
Config with example:
# Default: 8980, which port to create the server
servicePort: 8083
# Default: 0, open a port for prometheus monitoring tool, if set, user can check the
# performance using prometheus
monitorPort: 1234
# model path must be provided
modelPath: /home/yina/Documents/model/recys2021/wnd_813/recsys_wnd
# default: null, savedmodel input list if the model is tf savedmodel. If not provided, the inputs
# of the savedmodel will be arranged in alphabetical order
savedModelInputs: serving_default_input_1:0, serving_default_input_2:0, serving_default_input_3:0, serving_default_input_4:0, serving_default_input_5:0, serving_default_input_6:0, serving_default_input_7:0, serving_default_input_8:0, serving_default_input_9:0, serving_default_input_10:0, serving_default_input_11:0, serving_default_input_12:0, serving_default_input_13:0
# default: 1, number of models used in inference service
modelParallelism: 4
Feature Service Config#
Config with example:
load data into redis. Search data from redis
### Basic setting # Default: 8980, which port to create the server servicePort: 8082 # Default: null, open a port for prometheus monitoring tool, if set, user can check the # performance using prometheus monitorPort: 1235 # 'kv' or 'inference' default: kv serviceType: kv # default: false, if need to load initial data to redis, set true loadInitialData: true # default: "", prefix for redis key redisKeyPrefix: # default: 0, item slot type on redis cluster. 0 means slot number use the default value 16384, 1 means all keys save to same slot, 2 means use the last character of id as hash tag. redisClusterItemSlotType: 2 # default: null, if loadInitialData=true, initialUserDataPath or initialItemDataPath must be # provided. Only support parquet file initialUserDataPath: /home/yina/Documents/data/recsys/preprocess_output/wnd_user.parquet initialItemDataPath: /home/yina/Documents/data/recsys/preprocess_output/wnd_exp1/wnd_item.parquet # default: null, if loadInitialData=true and initialUserDataPath != null, userIDColumn and # userFeatureColumns must be provided userIDColumn: enaging_user_id userFeatureColumns: enaging_user_follower_count,enaging_user_following_count # default: null, if loadInitialData=true and initialItemDataPath != null, userIDColumn and # userFeatureColumns must be provided itemIDColumn: tweet_id itemFeatureColumns: present_media, language, tweet_id, hashtags, present_links, present_domains, tweet_type, engaged_with_user_follower_count,engaged_with_user_following_count, len_hashtags, len_domains, len_links, present_media_language, tweet_id_engaged_with_user_id # default: null, user model path or item model path must be provided if serviceType # contains 'inference'. If serviceType=kv, usermodelPath, itemModelPath and modelParallelism will # be ignored # userModelPath: # default: null, user model path or item model path must be provided if serviceType # contains 'inference'. If serviceType=kv, usermodelPath, itemModelPath and modelParallelism will # be ignored # itemModelPath: # default: 1, number of models used for inference # modelParallelism: ### Redis Configuration # default: localhost:6379 # redisUrl: # default: 256, JedisPoolMaxTotal # redisPoolMaxTotal:
load user features into redis. Get features from redis, use model at ‘userModelPath’ to do inference and get the user embedding
### Basic setting # Default: 8980, which port to create the server servicePort: 8085 # Default: null, open a port for prometheus monitoring tool, if set, user can check the # performance using prometheus monitorPort: 1236 # 'kv' or 'inference' default: kv serviceType: kv, inference # default: false, if need to load initial data to redis, set true loadInitialData: true # default: "" redisKeyPrefix: 2tower_ # default: 0, item slot type on redis cluster. 0 means slot number use the default value 16384, 1 means all keys save to same slot, 2 means use the last character of id as hash tag. redisClusterItemSlotType: 2 # default: null, if loadInitialData=true, initialDataPath must be provided. Only support parquet # file initialUserDataPath: /home/yina/Documents/data/recsys/preprocess_output/guoqiong/vec_feature_user.parquet # initialItemDataPath: # default: null, if loadInitialData=true and initialUserDataPath != null, userIDColumn and # userFeatureColumns must be provided #userIDColumn: user userIDColumn: enaging_user_id userFeatureColumns: user # default: null, if loadInitialData=true and initialItemDataPath != null, userIDColumn and # userFeatureColumns must be provided # itemIDColumn: # itemFeatureColumns: # default: null, user model path or item model path must be provided if serviceType # includes 'inference'. If serviceType=kv, usermodelPath, itemModelPath and modelParallelism will # be ignored userModelPath: /home/yina/Documents/model/recys2021/2tower/guoqiong/user-model # default: null, user model path or item model path must be provided if serviceType # contains 'inference'. If serviceType=kv, usermodelPath, itemModelPath and modelParallelism will # be ignored # itemModelPath: # default: 1, number of models used for inference # modelParallelism: ### Redis Configuration # default: localhost:6379 # redisUrl: # default: 256, JedisPoolMaxTotal # redisPoolMaxTotal:
Recall Service Config#
Config with example:
load initial item vector from vec_feature_item.parquet and item-model to build faiss index.
# Default: 8980, which port to create the server servicePort: 8084 # Default: null, open a port for prometheus monitoring tool, if set, user can check the # performance using prometheus monitorPort: 1238 # default: 128, the dimensionality of the embedding vectors indexDim: 50 # default: false, if load saved index, set true # loadSavedIndex: true # default: false, if true, the built index will be saved to indexPath. Ignored when # loadSavedIndex=true saveBuiltIndex: true # default: null, path to saved index path, must be provided if loadSavedIndex=true indexPath: ./2tower_item_full.idx # default: false getFeatureFromFeatureService: true # default: localhost:8980, feature service target featureServiceURL: localhost:8085 itemIDColumn: tweet_id itemFeatureColumns: item # default: null, user model path must be provided if getFeatureFromFeatureService=false # userModelPath: # default: null, item model path must be provided if loadSavedIndex=false and initialDataPath is # not orca predict result itemModelPath: /home/yina/Documents/model/recys2021/2tower/guoqiong/item-model # default: null, Only support parquet file initialDataPath: /home/yina/Documents/data/recsys/preprocess_output/guoqiong/vec_feature_item.parquet # default: 1, number of models used in inference service modelParallelism: 1
load existing faiss index
# Default: 8980, which port to create the server servicePort: 8084 # Default: null, open a port for prometheus monitoring tool, if set, user can check the # performance using prometheus monitorPort: 1238 # default: 128, the dimensionality of the embedding vectors # indexDim: # default: false, if load saved index, set true loadSavedIndex: true # default: null, path to saved index path, must be provided if loadSavedIndex=true indexPath: ./2tower_item_full.idx # default: false getFeatureFromFeatureService: true # default: localhost:8980, feature service target featureServiceURL: localhost:8085 # itemIDColumn: # itemFeatureColumns: # default: null, user model path must be provided if getFeatureFromFeatureService=false # userModelPath: # default: null, item model path must be provided if loadSavedIndex=false and initialDataPath is # not orca predict result # itemModelPath: # default: null, Only support parquet file # initialDataPath: # default: 1, number of models used in inference service # modelParallelism:
Recommender Service Config#
Config with example:
Default: 8980, which port to create the server
servicePort: 8980
# Default: null, open a port for prometheus monitoring tool, if set, user can check the
# performance using prometheus
monitorPort: 1237
# default: null, must be provided, item column name
itemIDColumn: tweet_id
# default: null, must be provided, column names for inference, order related.
inferenceColumns: present_media_language, present_media, tweet_type, language, hashtags, present_links, present_domains, tweet_id_engaged_with_user_id, engaged_with_user_follower_count, engaged_with_user_following_count, enaging_user_follower_count, enaging_user_following_count, len_hashtags, len_domains, len_links
# default: 0, if set, ranking service request will be divided
inferenceBatch: 0
# default: localhost:8980, recall service target
recallServiceURL: localhost:8084
# default: localhost:8980, feature service target
featureServiceURL: localhost:8082
# default: localhost:8980, inference service target
rankingServiceURL: localhost:8083
Run Java Client#
Generate proto java files#
You should init a maven project and use proto files in friesian gRPC project Make sure to add the following extensions and plugins in your pom.xml, and replace protocExecutable with your own protoc executable.
<build>
<extensions>
<extension>
<groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.6.2</version>
</extension>
</extensions>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>8</source>
<target>8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.6.1</version>
<configuration>
<protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.12.0:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact>
<pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId>
<pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.37.0:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact>
<protocExecutable>/home/yina/Documents/protoc/bin/protoc</protocExecutable>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>compile-custom</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Then you can generate the gRPC files with
mvn clean install
Call recommend service function using blocking stub#
You can check the Recommend service client example on Github
import com.intel.analytics.bigdl.friesian.serving.grpc.generated.recommender.RecommenderGrpc;
import com.intel.analytics.bigdl.friesian.serving.grpc.generated.recommender.RecommenderProto.*;
public class RecommendClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a channel
ManagedChannel channel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forTarget(targetURL).usePlaintext().build();
// Init a recommend service blocking stub
RecommenderGrpc.RecommenderBlockingStub blockingStub = RecommenderGrpc.newBlockingStub(channel);
// Construct a request
int[] userIds = new int[]{1};
int candidateNum = 50;
int recommendNum = 10;
RecommendRequest.Builder request = RecommendRequest.newBuilder();
for (int id : userIds) {
request.addID(id);
}
request.setCandidateNum(candidateNum);
request.setRecommendNum(recommendNum);
RecommendIDProbs recommendIDProbs = null;
try {
recommendIDProbs = blockingStub.getRecommendIDs(request.build());
logger.info(recommendIDProbs.getIDProbListList());
} catch (StatusRuntimeException e) {
logger.warn("RPC failed: " + e.getStatus().toString());
}
}
}
Run Python Client#
Install the python packages listed below (you may encounter pyspark error if you have python>=3.8 installed, try to downgrade to python<=3.7 and try again).
pip install jupyter notebook==6.1.4 grpcio grpcio-tools pandas fastparquet pyarrow
After you activate your server successfully, you can
Generate proto python files#
Generate the files with
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I../../protos --python_out=<path_to_output_folder> --grpc_python_out=<path_to_output_folder> <path_to_friesian>/src/main/proto/*.proto
Call recommend service function using blocking stub#
You can check the Recommend service client example on Github
# create a channel
channel = grpc.insecure_channel('localhost:8980')
# create a recommend service stub
stub = recommender_pb2_grpc.RecommenderStub(channel)
request = recommender_pb2.RecommendRequest(recommendNum=10, candidateNum=50, ID=[36407])
results = stub.getRecommendIDs(request)
print(results.IDProbList)
Scale-out for Big Data#
Redis Cluster#
For large data set, Redis standalone has no enough memory to store whole data set, data sharding and Redis cluster are supported to handle it. You only need to set up a Redis Cluster to get it work.
First, start N Redis instance on N machines.
redis-server --cluster-enabled yes --cluster-config-file nodes-0.conf --cluster-node-timeout 50000 --appendonly no --save "" --logfile 0.log --daemonize yes --protected-mode no --port 6379
on each machine, choose a different port and start another M instances(M>=1), as the slave nodes of above N instances.
Then, call initialization command on one machine, if you choose M=1 above, use --cluster-replicas 1
redis-cli --cluster create 172.168.3.115:6379 172.168.3.115:6380 172.168.3.116:6379 172.168.3.116:6380 172.168.3.117:6379 172.168.3.117:6380 --cluster-replicas 1
and the Redis cluster would be ready.
Scale Service with Envoy#
Each of the services could be scaled out. It is recommended to use the same resource, e.g. single machine with same CPU and memory, to test which service is bottleneck. From empirical observations, vector search and inference usually be.
How to run envoy:#
download and deploy envoy(below use docker as example):
download:
docker pull envoyproxy/envoy-dev:21df5e8676a0f705709f0b3ed90fc2dbbd63cfc5
run command:
docker run --rm -it -p 9082:9082 -p 9090:9090 envoyproxy/envoy-dev:79ade4aebd02cf15bd934d6d58e90aa03ef6909e --config-yaml "$(cat path/to/service-specific-envoy.yaml)" --parent-shutdown-time-s 1000000validate: run
netstat -tnlpto see if the envoy process is listening to the corresponding port in the envoy config file.For details on envoy and sample procedure, read envoy.